Before computing the GST liability on any article, it is necessary to understand other parts of the GST. For Example: Whether it is exempt from GST or is it covered in the Negative list or whether RCM applicable to such an article. Since the scope of the taxable supplies under GST is very wide, exemptions under GST have been clearly defined. In this article, we will understand the implication of exemption which is important because there are specific conditions that have been attached to it, for example, reversing the ITC.
Also, if today any article is being charged at a nil rate then it might be possible that the same article shall be charged at some higher rate in the future. Hence, It is important for us to understand the meaning and difference between the various terms such as Exempt, Nil Rated, Zero-rated, and Non-GST supplies.
What is the meaning of Exempt Supply?
As per the provisions of CGST Act, 2017, Exempted supplies means the following 3 kinds of supplies:
- Nil Rated Supply i.e. the supplies which have been specified at 0% rate
- Those supplies are exempted as per the order of the government by way of notification as per section 11 of the CGST Act, 2019. This notification shall become effective from the date of publishing it in the official gazette.
- Those supplies are not taxable under GST. For example 5 petroleum Products, Alcoholic liquor for human consumption.
There is no need to pay taxes on the above-specified supplies. Also, the Input Tax Credit (ITC) shall not be available to the recipient for utilization or setting off with the output liability.
Note: There is one more kind of supply which is Zero-rated supplies. Export supplies are called zero-rated supplies. Hence, it is to be noted that zero-rated supplies are not nil rated supplies. Under zero-rated supplies, the person is also eligible to claim the ITC or refund on such supply.
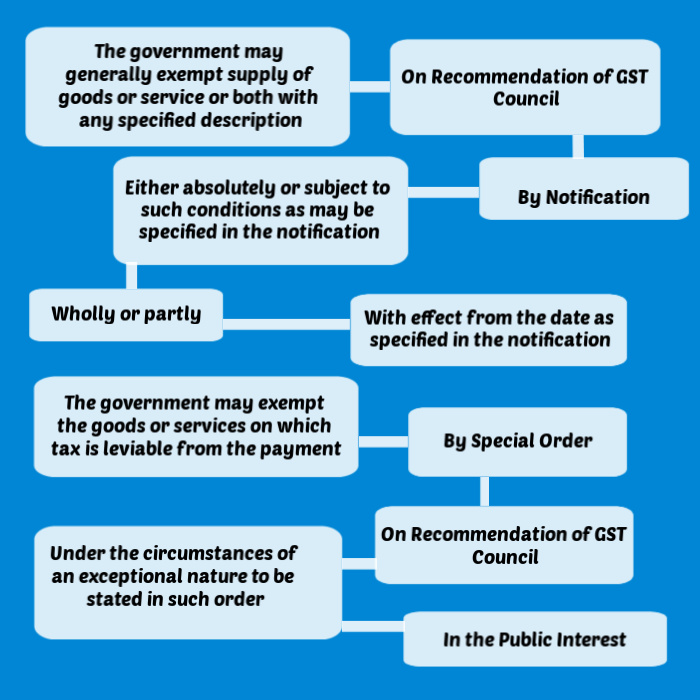
Section 11 empowers the Central or the State Governments to grant the exemption from GST. The exemption is granted on the recommendation of the GST council.
The exemption can be from the whole of the tax or part of the tax. It should be granted in the public interest.
The exemption can be granted to goods or services or both of any specified description by way of issuance of notification generally absolutely (i.e. unconditional exemption; exemptions which are not subject to any conditions) or conditionally (i.e. exemption is subject to specified conditions).
Exemptions may be granted by special order in case of the circumstance of an exceptional nature.
The absolute or unconditional exception is mandatory in nature. Where the supply of goods or services or both are unconditionally exempted from the whole of tax, the registered person does not have the option to collect and pay tax on such a supply of goods or services or both. Where the supply of the goods or services or both are unconditionally exempted from part of the tax, the registered person does not have the option to collect or pay the tax, in excess of the effective rate, on such a supply of goods or services or both.
Although, Where the exemption is conditional, it is the option of the registered person whether to avail the option or not by complying with the conditions as notified in the notification.
Let us understand this with the help of diagram:
Explanation about the exemption of any Article
The explanation has been inserted within 1 year from the date of notification to have retrospective effect: Where the government feels that there is need to clarify the scope or applicability of any notification or order issued under this section, it can issue explanation within 1 year of the issue of said notification or order. Such an explanation shall have effect as if it was there when the first notification or order was issued. In simple words, the explanation issued shall have an effect on a retrospective basis.
In the Exemption list of goods, the government has included the common items which have been used on a daily basis.
For Example, Unbranded Atta/ Maida/ Besan, unpacked food grains, milk egg, curd, lassi, and fresh vegetable.
As we have specified that the exemption granted by the government, can be conditional or unconditional. Let’s understand this with the help of some examples:
We will understand it with the example specified by the government in the notification vide notification number 09/2017 issued on 28.06.2017
Example:
Entry Number 1: Services by an entity registered under section 12AA of the Income-tax Act, 1961 by way of charitable activities.
Here, the meaning of charitable activities has been defined. So if the charitable entity is providing a charitable activity but which has not fallen under the definition as prescribed in the law, then such activity shall be liable for the GST.
Like conditional or unconditional, the GST exemption can be granted on absolute terms i.e without conditions or conditional exemption.
For Example:
Entry Number25: Transmission or distribution of electricity by an electricity transmission or distribution utility;
Entry Number 26: Services provided by the Reserve Bank of India.
Conditional Exemption: Exemption subject to certain conditions.
Example of Conditional Exemption:
Entry Number 12: Services provided by a hotel, inn, guest house, club or campsite, by whatever name called, for residential or lodging purposes, having tariff value of per room less than ` 1000/- per day shall be exempted from GST.
Important Note: Most of us think that there is only one Act in GST. Actually we have 34 Acts in GST. Confused, okay let understand this first:
1 Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017
31 Services Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017
1 Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017
1 GST Compensation Cess Act, 2017
For clarification: Each state has its own SGST Act. Although you may find most of the provision were the same written in each act but still if you are reading any provision in one act, it does mean that the same thing would be written on another act.
For this let me clarify that what we were reading above was specified in section 11 of the CSGT Act, 2017 and the same provision has been made under section of IGST Act, 2017.
As we already discussed above that on exempted supply, the recipient is not eligible to take the credit of such supplies.
Now let us understand, what we practically do:
First, we will take the whole amount of credit in return and then we will proportionality reverse ITC on exempted supply.
While discussing the exempted supply, we saw that one of the types of exempted supply is Non Taxable supply. So let’s see more about Non-taxable supply.
A Non-taxable supply is a supply of goods or services or both in which GST is not leviable under any Act.
To qualify the Non-taxable supply, it is compulsory that such a transaction should be a supply.
As per section 9(2) read with Schedule III, the list of items has been specified which shall be considered as Non Taxable supplies and these are:
- petroleum crude
- high-speed diesel
- motor spirit (commonly known as petrol)
- natural gas and
- aviation turbine fuel
It must be noted that these specified items are not out of the scope of GST. So, in the future, any or all of the items would be taxable at some rate.
The Negative list under GST
- Services by an employee to the employer in the course/ relation to employment
- Services of funeral, burial, crematorium or mortuary
- Sale of land
- Sale of completed buildings
- Actionable claims (other than lottery, betting, and gambling)
- Services by any court or Tribunal
- Functions performed by the MPs, MLAs, etc.
- Duties performed by any person who holds any post in pursuance of the provisions of the Constitution in that capacity.
Note: As per section 23 of the CGST Act, 2017, If a person is dealing in exclusively exempted supplies then he shall not be required to get the registration in the states in which he is providing such exempted supplies.
For Example, A person who is a trader in Delhi in which he is dealing in only tax-exempt supplies. His turnover during the year exceeds Rs.20 lakh, hence, in this case, he shall not be required for the registration under GST, since he is dealing with 100% exempt supplies.
Note: In case, a person is dealing in the exempted supply, then he cannot issue the Tax invoice because he is not eligible to charge GST on the invoice, hence, in this case, he shall issue Bill of supply.
For example: when a person supplies handloom, they have to issue a Bill of Supply instead of a tax invoice.
Note: There is no requirement to generate the e-way bill in case of movement of exempt supplies
Note: if a person has been registered and providing the exempted supplies then he shall be compulsorily required to file the GST return within the time as specified under the provisions of CGST Act, 2017 otherwise interest and fees shall be levied on him.


1 thought on “Implication of GST Exemption on Goods”