Goods and Services Tax (GST) is an Indirect tax levied on the supply of both goods or services.GST is a value-added tax as it is levied only on Value (i.e., increased value) which was added to the Product or Services during its life lifecycle. Input Tax Credit (ITC) is the Core concept of GST, Where credit of Inputs can be claimed to settle the output tax payable
What is IGST, CGST, SGST/UTGST?
GST was first introduced in France in 1954, Mainly to stop tax evasion due to higher tax rates. Present there are around 140 countries that have implemented GST System.
Federal structure nations like Canada, Brazil has adopted a Dual GST System
India has adopted the Canadian model Dual GST System, (where center and state has the power to levy and collect taxes) comprising of:
CGST: Central Goods and Services Tax levied & collected by Central Government.
SGST: State Goods and Services Tax, levied & Collected by State Government or Union Territory with State Legislatures.
UTGST: Union Territory Goods and Services Tax, levied & Collected by Union Territory without State Legislatures.
IGST: Integrated Goods and Services Tax.
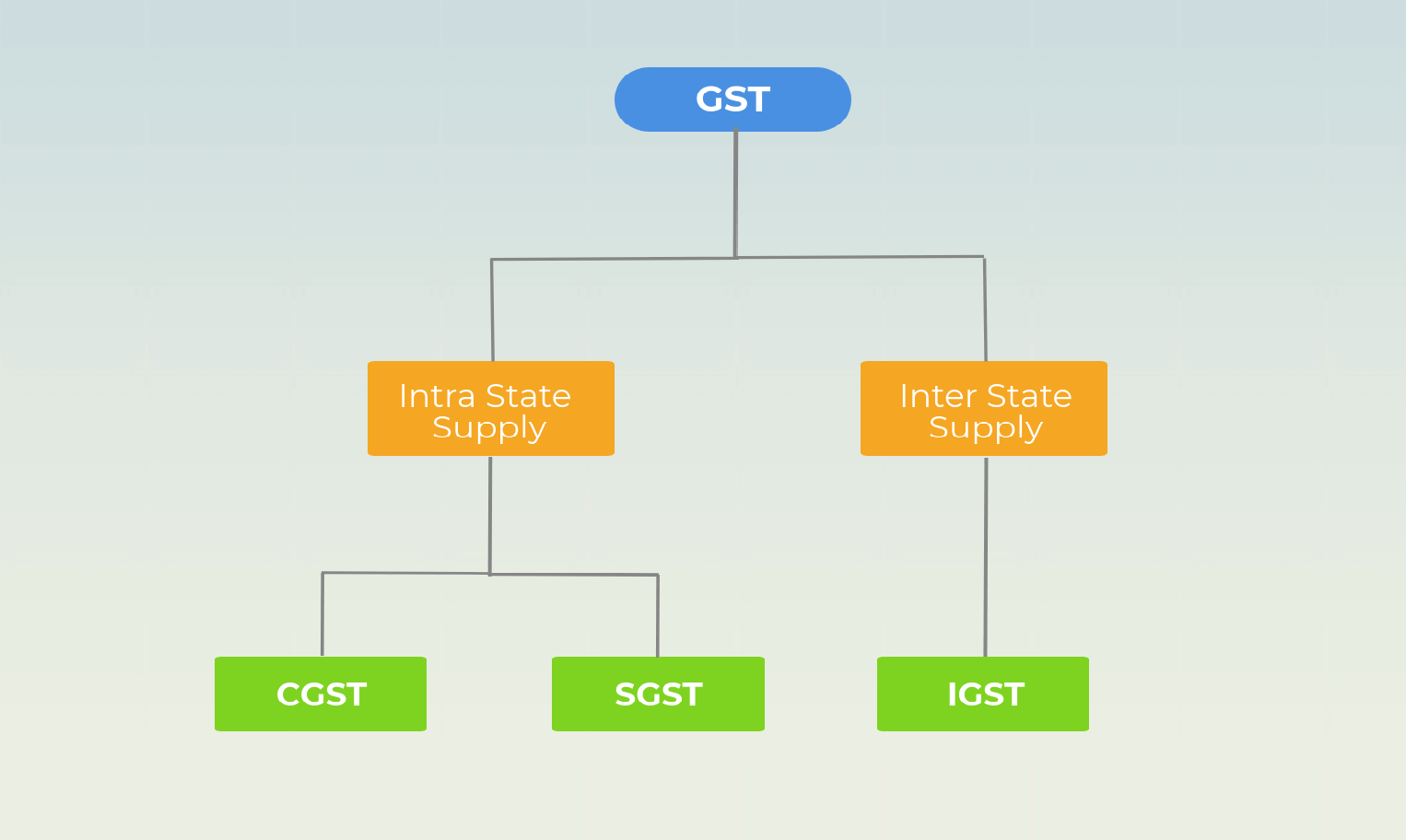
Determining Applicability of IGST, CGST, SGST/UTGST:
Applicability of CGST, SGST/UTGST or IGST is determined based on whether the Taxable Transaction is an Intra State Supply or Inter-State Supply.
Intra State Supply:
A Supply is considered as Intra State Supply only when both the location of Supplier & Place of Supply (i.e., place of the buyer) are in the same state/union territory.
CGST, SGST/UTGST is levied on Intra State Supply, as GST is a destination-based consumption tax, Tax will be collected by Consuming State.
Inter-State Supply:
A Supply is considered as Inter-State Supply when the location of Supplier & Place of Supply (i.e., place of the buyer) are in a different state/union territory.
IGST is levied on Inter-State Supply, later on, taxes will be distributed among State & Central Government
What is IGST?
As per section-9 of Integrated Goods and Services Act,2017, there shall be levied a tax called IGST(Integrated Goods and Services Tax) on all Interstate Supply of Goods or Services.
All Imports, Exports & Interstate Deemed Supply are liable to IGST under sec-9 of IGST act,2017. Since Interstate Supply of Goods or Services itself includes Imports, Exports & Interstate Deemed Supply.
Five Parameters of the GST Act:
- Supply of goods or services. Except for goods or services supply of anything does not attract GST
- Supply should be made for a consideration
- Supply should be made in the course or furtherance of business
- Supply should be made by a taxable person
- Supply should be a taxable supply
IGST tax was levied & collected by Central Government and proceeds of IGST will be apportioned between the center & states as per the article 269A.
The Value on which IGST levied shall be determined under section 15 of IGST act.
Maximum Rate of Tax levied under IGST shall not exceed 40%.
What is CGST?
As per section-9 of Central Goods and Services Act,2017, there shall be levied a tax called CGST (Central Goods and Services Tax) on all Intrastate Supply of Goods or Services.
The above-mentioned parameters were also applicable to CGST.
CGST tax was levied & collected by the Central Government on all taxable supply within the state.
The Value on which CGST levied shall be determined under section 15 of the CGST act.
Maximum Rate of Tax levied under CGST shall not exceed 20%.
What is SGST?
As per section-9 of State Goods and Services Act,2017, there shall be levied a tax called SGST (State Goods and Services Tax) on all Intrastate Supply of Goods or Services.
The above-mentioned parameters were also applicable to SGST.
SGST tax was levied & collected by State Government on all taxable supply within the state.
The Value on which SGST levied shall be determined under section 15 of the SGST act.
Maximum Rate of Tax levied under SGST shall not exceed 20%.
Why GST has been Split into CGST, SGST/UTGST or IGST?
Indian Constitution has the features of Federalism, whereby the powers of levying & collection of revenue has been distributed to both Centre & States, thereby ensuring Unity through Diversity. The concept of Unified/Single GST, curbs the powers of State government to levy & collect taxes, so, India has adopted dual GST model by implementing three types of tax structures, by facilitating Seamless Flow of Credit thereby removing cascading effect of taxes.
Types of Tax Structures:
- IGST
- CGST
- SGST/UTGST
Conclusion:
Implementing Dual GST in India with Seamless Flow of Credit eradicates the cascading effect of taxes which leads to decrease in the cost of goods or services thus increasing the competitiveness of goods or services in the market-leading to rise in GDP and Economy. End to END IT mechanism brings buoyancy to Government revenue.

6 thoughts on “GST and Its Different Types : IGST, CGST, SGST/UTGST”