In this article, we will discuss about...
Introduction
Taxation is an integral part of any economy, providing the government with the necessary funds to operate and deliver essential services. As a responsible citizen, it’s essential to understand the nuances of taxation, including concepts such as tax planning, tax avoidance, and tax evasion. Taxpayers often become confused due to the entanglement of these terms. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the distinctions between tax planning, tax avoidance, and tax evasion, particularly in the context of income tax in India.
Understanding Tax Planning
Tax planning is a legitimate and ethical process of organizing your finances to minimize tax liability while ensuring compliance with the tax laws and regulations of your country. It involves making informed financial decisions that take advantage of various tax incentives, deductions, and exemptions provided by the government. Effective tax planning allows individuals and businesses to optimize their tax liability without resorting to illegal or unethical practices.

The primary objective of tax planning is to strategically manage your financial affairs to legally reduce your tax burden. This can be achieved by making prudent investment choices, utilizing tax-saving instruments, and taking advantage of allowable deductions. For instance, in India, investments in schemes like Public Provident Fund (PPF), National Savings Certificate (NSC), and Equity-Linked Saving Scheme (ELSS) are some of the avenues for individuals to reduce their taxable income.
Consult CA Arun Tiwari for more information at 📞 8080088288 or cs@aktassociates.com
Exploring Tax Avoidance
Tax avoidance is the practice of arranging your financial affairs in a way that exploits legal loopholes and inconsistencies within the tax system to minimize tax liability. Unlike tax evasion, which involves deliberately concealing income or providing false information to tax authorities, tax avoidance stays within the bounds of the law. While tax avoidance may involve complex financial maneuvers, it remains a legitimate way of optimizing tax liability.

Tax avoidance can take various forms, such as restructuring business transactions, utilizing offshore accounts, or engaging in strategic financial planning. However, it’s important to note that tax avoidance strategies must not breach the spirit of the law or involve artificial arrangements solely for tax benefits. Courts often assess the substance of a transaction to determine its legitimacy in the eyes of the law.
Unpacking Tax Evasion
Tax evasion, on the other hand, is a serious offense that involves deliberately evading taxes by using illegal means. This can include underreporting income, inflating deductions, hiding money in offshore accounts, or providing false information to tax authorities. Tax evasion not only violates the law but also undermines the integrity of the tax system and leads to unfair distribution of the tax burden.

Tax evasion is a criminal act that can result in severe penalties, including fines and imprisonment. In India, the Income Tax Act imposes strict penalties for tax evasion, with the possibility of imprisonment ranging from six months to seven years, depending on the severity of the offense. Additionally, tax evaders may be required to pay back taxes, along with hefty fines.
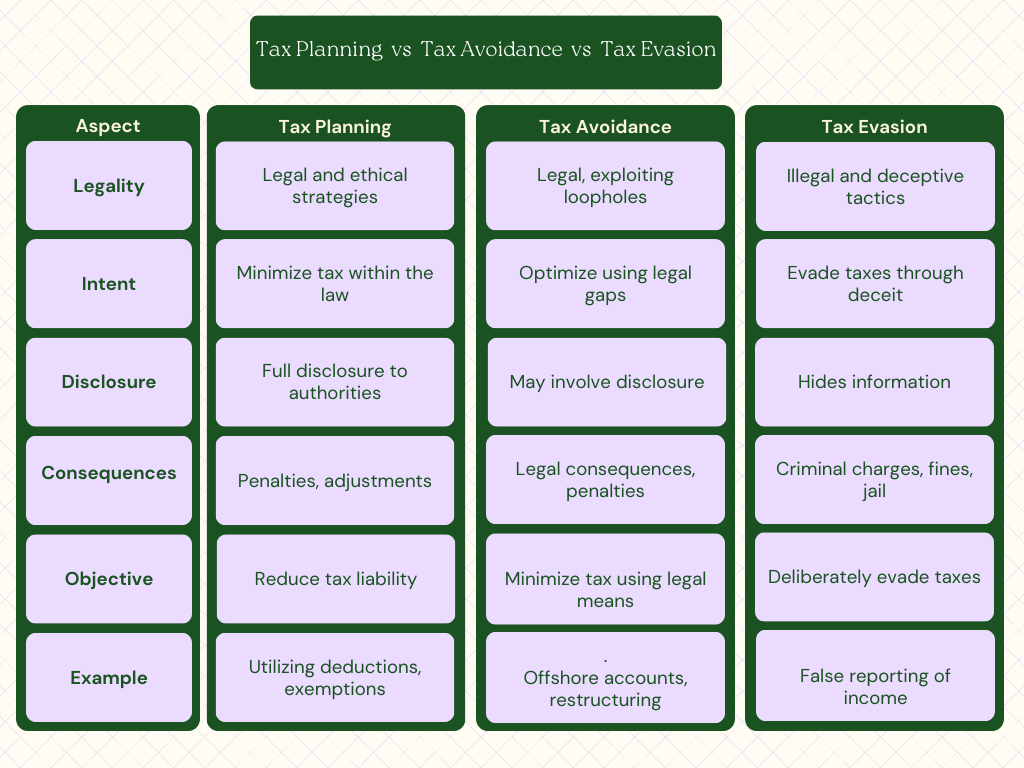
Distinguishing Factors
While tax planning, tax avoidance, and tax evasion may seem similar on the surface, there are clear differentiators that set them apart.
- Legality: Tax planning and tax avoidance are legal strategies employed to minimize tax liability. Tax evasion, however, involves illegal activities and deliberate attempts to deceive tax authorities.
- Intent: Tax planning is carried out with the intention of managing taxes within the boundaries of the law. Tax avoidance seeks to exploit legal loopholes, while tax evasion involves deliberate deceit.
- Disclosure: Tax planning involves full disclosure of financial information to tax authorities, ensuring transparency. Tax avoidance may involve disclosure but often emphasizes structures that reduce tax liability. Tax evasion, by contrast, involves hiding information to evade taxes.
- Consequences: Tax planning and tax avoidance have legal consequences limited to tax adjustments or penalties. Tax evasion can lead to criminal charges, substantial fines, and imprisonment.
Navigating Income Tax in India
In India, tax planning is highly encouraged by the government as a means to promote savings and investments. The Income Tax Act offers a plethora of tax-saving options for individuals, including deductions under Section 80C, exemptions for House Rent Allowance (HRA), and deductions for medical insurance premiums under Section 80D.
However, Income Tax Department takes tax evasion extremely seriously. The Indian government has implemented robust measures to curb tax evasion, such as the introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) and the use of technology to track financial transactions. The government has also entered into various international agreements to exchange financial information with other countries to combat tax evasion more effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the distinctions between tax planning, tax avoidance, and tax evasion is crucial for responsible financial management. While tax planning and tax avoidance are legitimate ways to minimize tax liability, tax evasion involves illegal activities and serious consequences. As taxpayers, it is our duty to engage in ethical and legal financial practices, ensuring that we contribute to the development of our nation through responsible tax compliance.

