Introduction:
When individuals and businesses sell a property, they must consider the implications of capital gains tax. However, the Indian Income Tax Act offers provisions to mitigate the tax burden for taxpayers who reinvest the proceeds from property sales into specific assets. Sections 54, 54EC, and 54F of the Income Tax Act provide tax benefits to individuals who fulfill certain conditions while reinvesting in residential properties or specified assets. In this article, we will delve into the details of these sections and explore the benefits they offer.
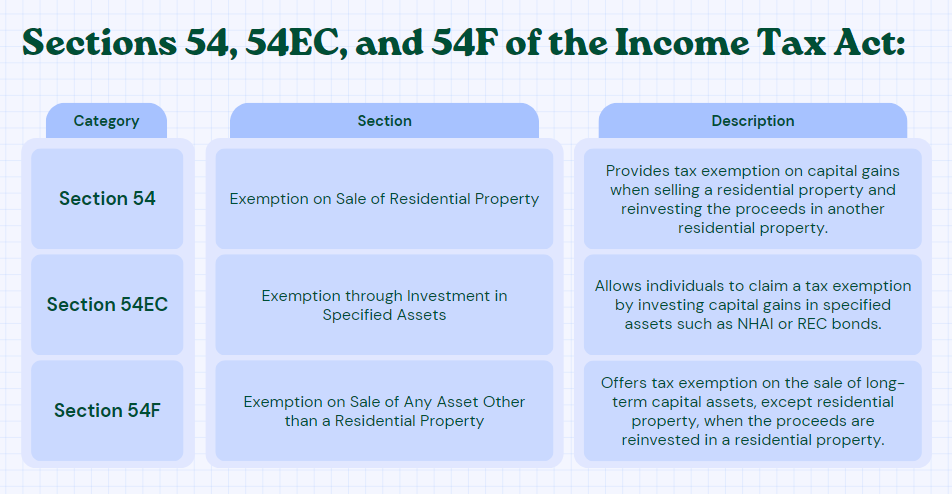
Section 54: Exemption on Sale of Residential Property:
Section 54 of the Income Tax Act allows individuals to claim an exemption from capital gains tax if they sell a residential property and reinvest the proceeds in another residential property. This section operates under the following key conditions:
- Type of Property: Individuals must sell a residential house and subsequently purchase a residential house.
- Timeframe for Purchase: The new property must be purchased either one year prior to the sale or within two years from the sale date. Alternatively, individuals can construct a new residential property within three years of the sale.
- Investment Amount: Individuals must utilize the entire sale proceeds or the capital gain amount to purchase the new property. If the entire amount is not reinvested, the exemption will be proportionally reduced.
- Holding Period: The new residential property must be held for at least two years from the date of acquisition to avail of the tax exemption. Selling the property within two years will result in the exempted amount being added to the income in the year of sale.
Consult CA Arun Tiwari for more info at 📞 8080088288 or cs@aktassociates.com
Section 54EC: Exemption through Investment in Specified Assets:
Section 54EC provides individuals with an opportunity to claim a tax exemption by investing capital gains in specific assets, namely notified bonds issued by the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) or the Rural Electrification Corporation (REC). The key points to note are:
- Investment Timeframe: Individuals must invest the capital gains within six months from the date of property transfer to claim the exemption.
- Maximum Investment Limit: The maximum amount that can be invested under Section 54EC is ₹50 lakh.
- Holding Period: Individuals must hold the specified assets for a minimum of five years. Selling them within five years will result in the exempted amount being added to the income in the year of sale.
- Eligibility: Only long-term capital gains are eligible for exemption under Section 54EC. The property being sold must have been held for at least two years.
Section 54F: Exemption on Sale of Any Asset Other than a Residential Property:
Section 54F allows individuals to claim an exemption on the sale of any long-term capital asset other than a residential property. The key provisions are as follows:
- Reinvestment in Residential Property: Individuals must utilize the proceeds from the sale to purchase a residential property.
- Timeframe for Purchase: The new residential property must be purchased either one year before the sale or within two years from the sale. Alternatively, individuals can construct a new residential property within three years of the sale.
- Investment Amount: Individuals must invest the entire sale proceeds or the capital gain amount in the new residential property. If the entire amount is not reinvested, the exemption will be proportionally reduced.
- Holding Period: Individuals must hold the new residential property for at least three years from the date of acquisition. Selling it within three years will result in the exempted amount being added to the income in the year of sale.

Conclusion:
Sections 54, 54EC, and 54F of the Income Tax Act provide taxpayers in India with opportunities to reduce their tax liability when selling properties or other long-term capital assets. By adhering to the specific conditions outlined under each section, individuals can avail of tax exemptions on capital gains by reinvesting in residential properties or specified assets. It is essential to consult with a tax professional or chartered accountant to ensure compliance with the provisions of the Income Tax Act and make the most of these beneficial sections.