For Income Tax purpose in India, the taxability of income of any person depends on the person’s residential status. To levy a tax on any income, the residential status of the person needs to be determined. On the basis of the residential status, the income of the person shall be taxable.
In case of an individual: If the person is a resident and ordinary resident then his income, whether received or accrued in India or outside India, shall be taxable.
In Case of a Non-Resident Indian (NRI), only the income which accrues or arises to him in India shall be taxable.
For a Resident but Not Ordinary Resident (RNOR), income which accrues or is received outside India from a business not controlled from India or a profession not setup in India shall not be taxable.
The residential status in case of individuals is determined on the basis of a number of days of his stay in India, whereas in case of HUF/Firms and Companies residential status is determined on the basis of the location from where the control and management of affairs are carried out.
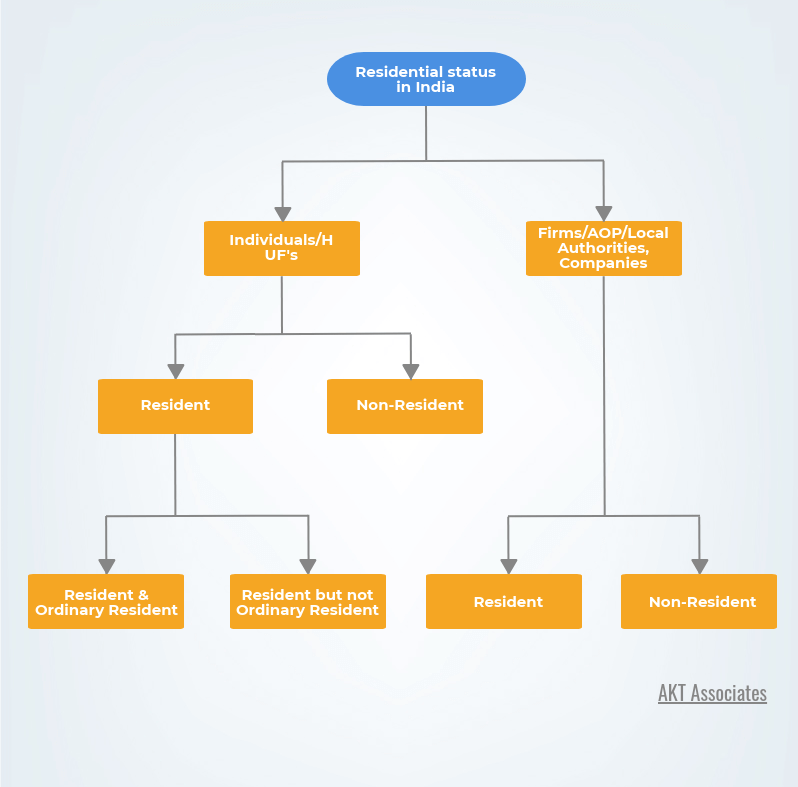
In this article, we will discuss about...
Let us first understand a few terms relevant to the residential status of an individual:
Citizen of India: Citizen of India in simple terms means a person born in India or a person who’s both parents or either of them is Indian citizens and are not illegal immigrants at the time of his birth.
Person of Indian origin: A person shall be deemed to be of Indian origin if he, or either of his parents or any of his grandparents, were born in undivided India.
Previous Year: As per Income Tax Act, Previous Year means the financial year immediately preceding the Assessment Year. The residential status of an individual is determined on the basis of a number of days of his stay in the Previous Year. Income tax is levied on the income earned in the Previous Year.
Assessment Year: As per Income Tax Act Assessment Year is a period of twelve months commencing on 1st April every year. Assessment of the income earned in the Previous Year is carried out in the Assessment Year.
Residential Status of an individual:
A resident of India:
An Individual will be a Resident of India in any previous year if
He stays in India for 182 days or more in the current Previous Year
OR
He stays in India for 60 days or more in the current Previous Year and 365 days or more in preceding 4 Previous Years.
In case of an Individual being an Indian citizen, who leaves India for employment outside India.
OR
An Indian citizen being a crew member of an Indian ship leaves India during the previous year.
OR
An Indian citizen or a Person of Indian Origin who is engaged outside India in any employment or Business or Profession and is visiting India during the previous year,
Then the above condition of only 182 days of stay in India shall apply to him, i.e. the second condition of 60 days or more in the previous year and 365 days in preceding 4 previous years shall be ignored.
Non-Resident:
An individual who does not fulfill the above basic conditions of residential status shall be a Non-Resident.
Resident and Ordinary Resident (ROR):
Once an individual fulfills the basic condition of residential status then we identify whether he is a Resident and Ordinary Resident
An Individual shall be Resident and Ordinary Resident of India if he fulfills both the below conditions:
He is a resident in any 2 or more previous years out of last 10 previous years preceding the relevant previous year
AND
His total stay in India in the last 7 previous years preceding the relevant previous year is 730 days or more.
Resident but Not Ordinary Resident (RNOR):
If an individual is a Resident but has not fulfilled both the above conditions required to be qualified as a Resident and Ordinary Resident then the individual shall be a Resident but Not Ordinary Resident.
The above determination of the residential status of an individual as Resident, Resident and Ordinary Resident, Resident but not Ordinary Resident and Non-Resident is required for assessing the income of the individual.
Let us clear the concepts with the below examples:
Example 1: In the PY 2018-19, Ram leaves India for employment in London on 12th August 2018. He returns to India on 24th April 2019. What is Ram’s residential status for the PY 2018-2019?
Ram’s stay in India in the PY 2018-2019, from 1st April 2018 to 12th August 2018 is 134 days which is less than 182 days, thus Ram is a Non-Resident for the P.Y. 2018-19.
If Ram would have left India on 10th October 2018 then his stay in India would have been 193 i.e. more than 182 days, making him a Resident for the P.Y. 2018-19
Example 2: Mr. John an Australian businessman visits India for the business purpose for 100 days in every financial year. This has been his practice for the last 10 years. What is his residential status for PY 2018-2019?
Period of stay in the PY 2018-19 = 100 days
Period of stay in the preceding 4 previous years
| Year | No. of days |
| 2017-18 | 100 |
| 2016-17 | 100 |
| 2015-16 | 100 |
| 2014-15 | 100 |
| Total | 400 |
Total stay in last 4 preceding previous years = 400 days
Mr. John’s stay in PY 2018-19 is 100 days i.e. more than 60 days and total stay in last 4 preceding previous years is 400 days i.e. more than 365 days, therefore Mr. John is a Resident in the PY 2018-19.
Mr. John’s stay in last 7 years preceding the current previous year
| Year | No. of days |
| 2017-18 | 100 |
| 2016-17 | 100 |
| 2015-16 | 100 |
| 2014-15 | 100 |
| 2013-14 | 100 |
| 2012-13 | 100 |
| 2011-12 | 100 |
| Total | 700 |
Mr. John’s stay in last 7 preceding years is 700 days i.e. less than 730 days, therefore, Mr. John is a Resident but Not Ordinary Resident for the PY 2018-19.
Assessment of Income on the basis of Residential Status:
If the Individual is a Resident and Ordinary Resident then income earned, accrued or received by him whether in India or outside India shall always be taxable in India.
If the Individual is a Resident but Not Ordinary Resident then the income which accrues or arises or is received by him outside India shall not be taxable in India, however if the income is received, earned or accrues to him outside India but on account of business controlled from India or profession set up in India then such an income shall be taxable in his hands in India.
If an Individual is a Non-Resident then any income which is earned accrues or is received by him outside India whether or not from a business controlled from India or profession set up in India, the income shall not be taxable in his hands in India.
The above points have been summarized in the below table
Taxability of an Individual in India
| Source of Income | Resident and Ordinary Resident | Resident but Not Ordinary Resident | Non-Resident |
| Income received or deemed to be received in India | √ | √ | √ |
| Income accrues or arises or is deemed to accrue or arise in India | √ | √ | √ |
Income accrues or arises or is received outside India from
|
√ | √ | X |
| Income accrues or arises or is received outside India | √ | X | X |


10 thoughts on “Residential Status of a Non-Resident Indian (NRI) and Tax Incidence in India”